Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a fairly common disease. Like other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, in recent years this disease has become younger - it is observed in middle-aged and sometimes young people. And although among all parts of the thoracic region it is the least susceptible to injury, due to the mobility of the position of the vertebrae, this disease is becoming more common in men, women and even children. That is why osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a disease whose symptoms and treatment are of interest to many.
What are the specific characteristics of the thoracic spine?
The thoracic spine does not support as much load as the lumbar spine and its mobility is less than that of the cervical spine. Because of this, in the thoracic spine, symptoms of osteochondrosis and other diseases appear at later stages than in other parts of the spine. According to statistics, the thoracic spine is the least susceptible to injuries, damage and diseases, such as intervertebral hernia and vertebral displacement. However, there are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing illnesses and injuries, for example, scoliosis and poor posture. In thoracic osteochondrosis, as in any other disease, the disease can usually only be detected after significant development.
Symptoms and signs of thoracic osteochondrosis
Thoracic osteochondrosis can be easily distinguished from other diseases by the characteristic symptoms of the disease. There are the following signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region:
- Due to prolonged stay in the same position, chest pain occurs - it manifests itself with sudden movements or significant physical activity;
- Inhaling and exhaling deeply causes pain and tightness in the middle of the back;
- When raising your arms and making sharp turns, a stable pain syndrome is noted;
- Moderate pain is constantly observed in the shoulder blade region;
- Certain parts of the body become numb and insensitive;
- Unreasonable tingling or chills;
- Itching or burning sensations in the legs, decreased temperature in relation to the rest of the body;
- The disease causes side effects such as digestive disorders, intercostal neuralgia and reproductive problems.
Depending on the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region that appear during the development of the disease, the disease can be confused with other, no less serious diseases, such as pneumonia, angina pectoris. Therefore, for any of the indicated signs of osteochondrosis, a comprehensive examination of the body is necessary.

Pain in this disease is divided into two types:
- Dorsago - acute pain of significant intensity, accompanied by a feeling of stiffness and interfering with normal breathing;
- Dorsalgia – pain in the region of the intervertebral discs that lasts a long time.
One of the most striking manifestations of the disease is pain in the epigastric region. Pain exacerbations occur regardless of the season, usually caused by diet.
Causes of thoracic osteochondrosis
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine may be different. Among the most common manifestations are the following:
- Pathologies of the structure of intervertebral discs, including a hereditary tendency to develop spinal diseases;
- Thin intervertebral discs, hernias;
- Decrease in the quality of cartilaginous tissue;
- Circulatory disorders that impede blood flow to the spinal cord;
- Unreasonable load on the spine, causing degeneration of muscle tissue, cartilage or bones;
- Lack of vitamins and microelements, especially calcium;
- Constant physical activity;
- Sedentary lifestyle, working in front of the computer or driving a car;
- Injuries and other damage to the spine.

Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine should begin as early as possible. Even if no manifestations in the form of significant pain are detected, this does not mean that the disease does not require treatment. The sooner treatment is started, the easier and faster it will be. Modern medicine offers a wide range of methods for treating osteochondrosis, and in combination with traditional medicine methods, quick and lasting results can be achieved.
The first stage of treatment is diagnosis. It is necessary to accurately determine the disease - for this, the doctor performs palpation, examination and collects anamnesis. To accurately determine the cause of the disease, it is necessary not only to take blood and urine tests, but also to do X-rays or MRI.
When the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor determines how to treat osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. The usual course includes not only drug treatment, but also physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage.
Exercise therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis
Exercise therapy for this disease is mandatory, as is massage, but the basis of treatment in any case is medication. The doctor treats osteochondrosis according to the patient's specific case.

Manual therapy
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis will be more complete if, in addition to regular massage and physical education, it includes manual therapy. It helps to eliminate increased muscle tone, eliminate spasms, and also restore the normal position of the back muscles. A chiropractor can relieve back tension, free up blood vessels for improved blood supply, quality nutrition, and restore intervertebral discs.
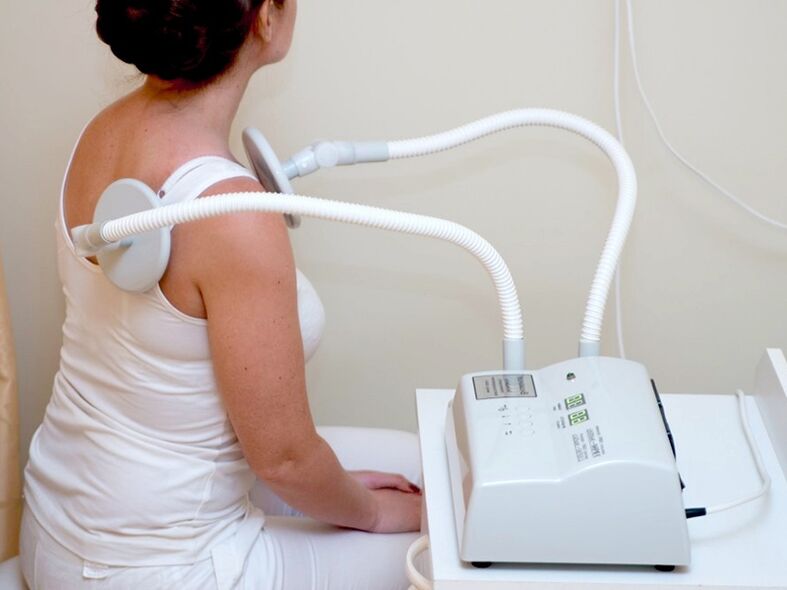
Physiotherapy
Drug therapy is often combined with physiotherapeutic methods. Usually patients are prescribed:
- Shock wave treatment is the effect of sound waves on the thoracic region. Improves metabolism, blood supply to the affected area, improves tissue restoration and relieves pain;
- Detensor therapy – helps to unload the spine and relieve spasms under the influence of the patient's own weight;
- Electrotherapy – heating tissues using electrical fields, delivering impulses to improve blood circulation and stimulate metabolism. Under the influence of current, drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis are absorbed more efficiently;
- Ultraviolet treatment – quartz treatment increases the production of vitamin D, in addition to helping to relieve pain and improve the functioning of the immune system;
- Magnetotherapy - a low-frequency electromagnetic field improves the supply of useful substances to the diseased area, accelerates healing and improves blood flow;
- Laser therapy – lasers can relieve spasms and pain, reduce inflammation, stimulate tissue repair processes;
- Ultrasound – Ultrasonic vibration helps relieve pain, inflammation and also promotes better absorption of medications.
Drug therapy
For this disease, drug treatment may include medications for internal use and topical application.
Tablets for osteochondrosis allow:
- Reduce pain;
- Relieve inflammation;
- Relax your muscles;
- Improve local blood circulation;
- Restore metabolism;
- Strengthen tissue regeneration.
Symptomatic treatment is very important for this disease. First, take painkillers. They allow you to get rid of the pain that sometimes accompanies every movement. To ensure that the medicine not only relieves pain, but also reduces inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with an analgesic effect are recommended. In addition, for osteochondrosis, it is recommended to use chondroprotective drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulatory agents.
Local medicines for the treatment of the disease are aimed at the same effect as internal medicines. Ointments, gels and creams for application to the affected area may contain analgesics and NSAIDs, as well as chondroprotectors and other necessary agents.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine helped in the treatment of osteochondrosis long before all modern medicines were invented. Its effectiveness is not that high, but side effects are absent or minimal. Folk remedies are an excellent addition to the main treatment and, as part of complex therapy, allow for faster recovery.

Among the popular remedies are:
- Horseradish leaves, soaked in boiling water, are applied to the diseased area - this relieves the symptoms of osteochondrosis, and regular procedures prevent exacerbation of the disease;
- A compress of homemade cottage cheese with a few drops of vinegar is applied overnight to eliminate the symptoms of osteochondrosis in the chest or neck;
- A tincture of the leaves and flowers of the coltsfoot plant is used to rub the affected area;
- Fresh rye flour cakes are slightly cooled and applied to sore spots to relieve inflammation and pain.
Offers traditional medicine and medicines for internal use. For thoracic osteochondrosis you can use:
- Four cloves of garlic and three crushed lemons, poured with boiling water, are taken on an empty stomach, one tablespoon at a time. Cannot be used for gastritis and peptic ulcers;
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves at the rate of one tablespoon per liter of boiling water is taken instead of regular tea;
- Horse sorrel boiled for ten minutes. Leave it for a few hours and then take a few inns three times a day. This is an effective remedy for pain in osteochondrosis;
- Nettle juice. Mixed in equal proportions with honey and ethyl alcohol, take a tablespoon three times a day for a week and a half.
What to do in case of an exacerbation?
Exacerbations are the hardest part of this disease. They are accompanied by sharp, sharp pains, called dorsago. It is very difficult to relieve such intense pain and it is not always possible to do it alone. The cause of the exacerbation may be:
- Hypothermia;
- Physical exercise;
- Overwork, constant hard work;
- Very active training;
- Stress and other nervous system tensions.

What should a person do if they feel that an exacerbation is approaching? First of all, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist. He will diagnose your condition and prescribe the necessary treatment measures that will help eliminate the exacerbation and minimize its symptoms. Exacerbation of the disease is often accompanied by nausea, high-intensity headaches, limited mobility and general weakness.
Since this disease is closely related to breathing, an exacerbation can cause difficulties - deep breaths and sharp exhalations become very painful. To minimize the number of muscle spasms, it is recommended to observe bed rest during an exacerbation.
Patients with a worsening of the disease are sent to hospital, where they are transported in an ambulance so that the patient does not need to move around much. During treatment, medications are first prescribed to relieve muscle spasms. To relieve pain, analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy are prescribed.
One of the most serious consequences of an exacerbation of the disease can be an intervertebral hernia. A slight protrusion in the thoracic spine can cause pain in different parts of the back. If the protrusion is large, it can cause serious problems and put the patient's life in danger. The only way to get rid of an intervertebral hernia in this case is surgery.
To avoid such complications during an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to follow the rules:
- Maintain bed rest, minimum physical activity and unnecessary movements;
- Maintain a healthy diet;
- Compliance with all doctor's recommendations, taking prescribed medications;
- Massage and rub the affected area;
- On the recommendation of a doctor - exercise therapy;
- Rubbing gels, ointments and creams prescribed by a doctor into the chest and spine area;
- Attendance at physiotherapy procedures prescribed by your doctor.
Prevention measures
Thoracic osteochondrosis is an unpleasant disease that must be avoided. To reduce your risk of developing the disease, you should:
- Avoid lifting weights beyond normal limits;
- Protect the spine from hypothermia;
- Rest regularly and avoid excessive tiredness;
- Make sure your posture is correct.
- Don't stay in the same position for too long, especially if it's uncomfortable.
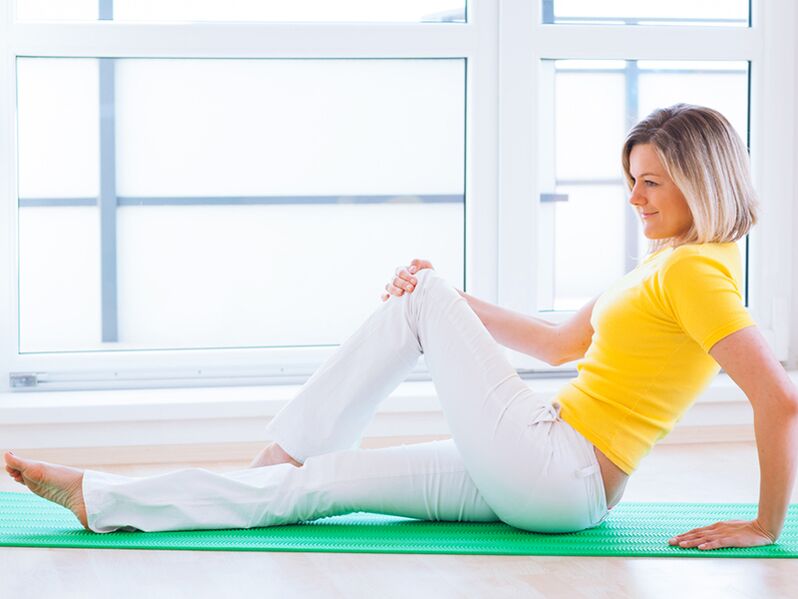

If your professional activity inevitably involves remaining in the same position, it is necessary to adopt a rule regarding physical exercise. Office workers, drivers and other professionals who sit in one place for a long time need to get up regularly, change the position of their spine and stretch their legs. If possible, during these physical minutes, one of the sets of exercises specially developed for such cases is performed.
It is equally important to eat properly and nutritiously. The basic principle of a healthy diet for the musculoskeletal system is to avoid salty foods. Salt is deposited in bone and cartilage tissue, causing its destruction.
It is best to sleep on orthopedic mattresses. If this is not possible, it is better to sleep on a hard surface than on a very soft surface. You can place a special sign on the bed or sofa.